As of April 30, 2025, we’re proud to announce our exciting new chapter. | Read more here.
More than ever, the construction industry is embracing digital transformation, and at the heart of this change is building information modeling (BIM). As projects become more complex and the demand for efficiency grows, understanding the BIM process is essential for professionals working in architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC). This article will break down the essentials of the BIM process, explore its key components, and highlight how it is revolutionizing project management.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a complex 3D modeling tool that helps streamline every aspect of design and construction. However, using it effectively requires a strong strategy and extensive planning. This is where a BIM process comes in.
The BIM process involves creating, managing, and sharing digital representations of a building’s physical and functional characteristics throughout its lifecycle. This methodology defines workflows, decision-making, and project management in the AEC industry by providing stakeholders with real-time access to critical information.
There is no one correct way to use BIM. Every firm will vary in its approach to a BIM process. However, there are four essential components to any essential strategy: a capable BIM software platform, a shared data environment, effective collaboration, and good communication,
BIM software, such as Autodesk Revit, is at the heart of the BIM process. These tools enable the creation of detailed 3D models that serve as digital representations of a building. The BIM model incorporates data from various disciplines, including architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing), allowing for a more complete view of the building design. BIM software allows project teams to run simulations, perform clash detection, and generate cost estimations, all within a single platform.
Another essential component of an effective BIM process is information accessibility. A common data environment (CDE) ensures that all project team members have access to the same data, reducing the risk of errors and rework. This “single source of truth” provides a comprehensive view of the project at any stage of the construction process, from pre-design to facility management. The ability to exchange information efficiently among stakeholders also improves the overall efficiency and accuracy of the project.
A good BIM process is centered around collaboration among all team members involved in a construction project. Whether it’s architects, civil engineers, or construction teams, BIM standards ensure that everyone is on the same page. The digital model created in the design phase acts as a central reference point, enabling seamless communication and coordination among team members. This collaborative approach is particularly beneficial in complex projects where integrating various disciplines is crucial for success.
Communication is vital in any project, and the BIM process enhances this by providing clear and accessible information to all stakeholders. Through BIM, everyone involved in the project can visualize the building design and see how changes in one area affect the overall project. This transparency helps firms make informed decisions, minimize delays, and ensure the project stays on track.
The pre-design phase is the foundation of the BIM process. Project requirements are defined during this stage, and initial concepts are developed. BIM technology is used to create early models that help stakeholders visualize the building design and explore various options. This phase is critical for establishing the project’s goals, budget, and timeline.
In the design phase, the BIM model evolves into a detailed digital representation of the building. Autodesk Revit and other BIM tools are used to create comprehensive 3D models that incorporate architectural, structural, and MEP elements. This phase involves iterative design and real-time collaboration, allowing for adjustments and refinements as needed. The design phase is where simulations, clash detection, and sequencing are performed to ensure that the building design is feasible and efficient.
The construction phase is where the digital model really comes to life. Engineers use BIM models to guide on-site construction, ensuring the building is built according to the design specifications. The use of BIM in construction management allows for better sequencing, coordination, and progress monitoring. Any issues that arise on-site can be quickly addressed by referring to the BIM model, reducing the likelihood of costly delays and rework.
BIM extends beyond the construction phase into facility management as well. The BIM model serves as a valuable resource for maintaining and operating the building throughout its lifecycle. Information related to maintenance schedules, renovations, and future upgrades is stored in the BIM model, providing a comprehensive record for facility managers. This phase highlights the sustainability benefits of BIM, as it enables more efficient resource management and reduces the building’s environmental impact.
Taking advantage of a BIM process brings many benefits, making it a game changer in the AEC industry. Some of these benefits include:
While the benefits of BIM are many, implementing BIM certainly comes with its challenges, Including:
Understanding the BIM process is crucial for AEC professionals looking to stay competitive in a rapidly changing industry. From the pre-design phase to facility management, BIM offers a comprehensive approach to managing construction projects more efficiently and sustainably. While implementing BIM comes with its challenges, its benefits in terms of collaboration, visualization, and overall project management make it a valuable tool for the future of design and construction.
Welcome architects, engineers, and BIM enthusiasts! Are you excited to dive into the latest features of Revit 2025?
This update brings a wave of enhancements designed to supercharge your design productivity, elevate your sustainability efforts, and empower you to create clear, well-organized documentation.
Let’s explore some of the most architecturally significant improvements across these key areas.
Revit 2025 streamlines your modeling process, freeing you to focus on creative problem-solving. Here are some highlights:
Revit 2025 equips you with the tools to make informed decisions for a greener future:
Creating clear and organized documentation just got easier with Revit 2025’s documentation efficiency enhancements:

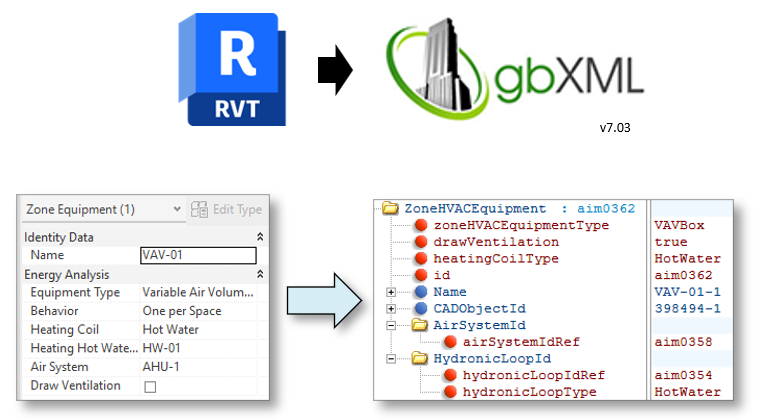
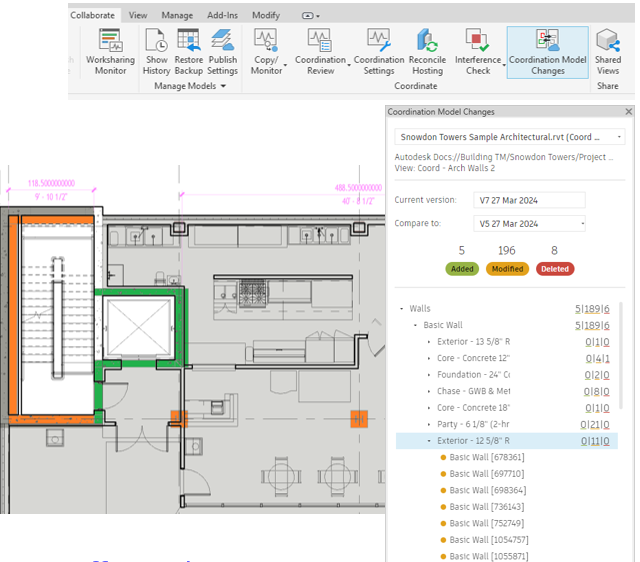
Revit 2025 strengthens collaboration throughout the project lifecycle with improved interoperability features:
Revit 2025 offers a compelling array of architectural and platform improvements designed to empower you to design more efficiently, sustainably, and collaboratively. From the effortless creation of complex models to the seamless generation of clear documentation sets, Revit 2025 is poised to revolutionize the way you approach BIM projects.
If this blog post has piqued your interest in the exciting possibilities offered by Revit 2025, you can also watch this video recording of our webinar about the latest features!
Stay tuned for future posts where we delve deeper into specific features and showcase their practical applications in real-world design scenarios. Happy designing!
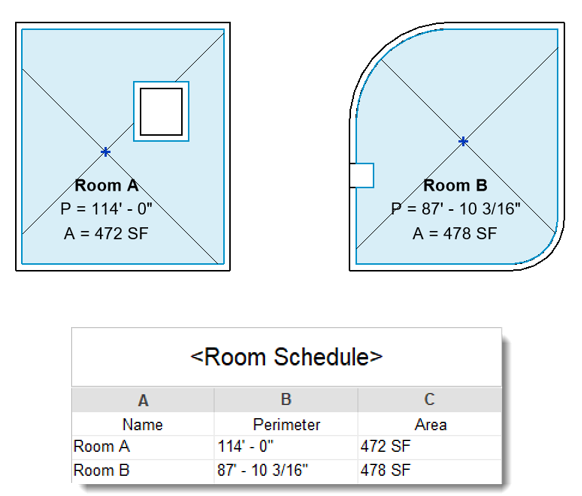
Revit is an excellent tool for creating detailed architectural models, and one of its key features is the ability to apply a color scheme to your project. A well-designed color scheme can make your model look more visually appealing and help communicate design intent to clients and stakeholders.
By applying custom color schemes to the rooms, walls, and other elements of your model, you can easily differentiate between different types of spaces, such as living areas or utility rooms.
I often use this feature to swiftly color-code different rooms in a floor plan based on their area or name. In this blog post, I will show you how to create a Revit color scheme that will enhance your architectural models.
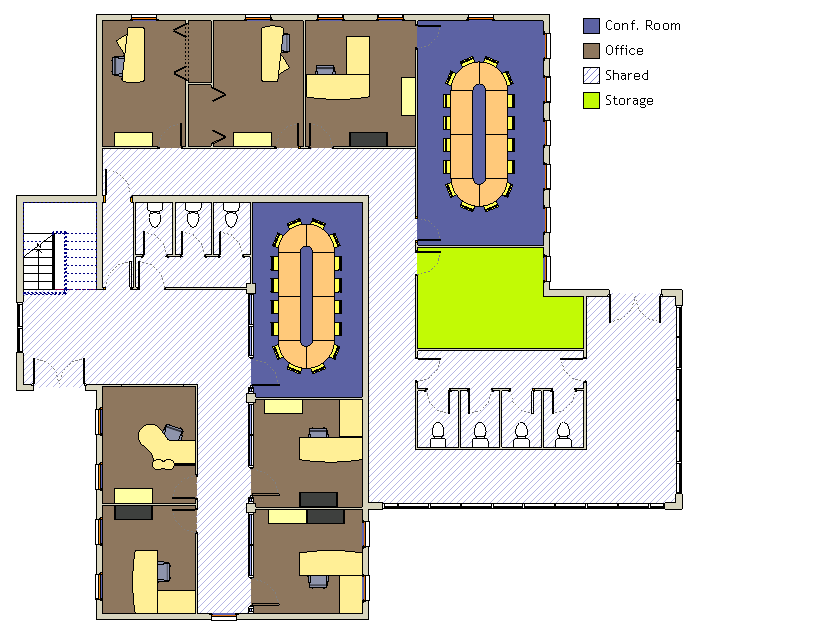
Your first step is to create the area where you want to apply the color scheme. This can be done by using bounding elements, which are building components such as walls or floors that enclose a space.
If you already have an enclosed space, bounded by walls or columns, you can simply select the Room tool in Revit and click on the space to create a room. This will automatically create a room that fits into the bounding elements. If you do not have any bounding elements, you will first need to create them before proceeding.
Once you have the bounding elements and rooms in place, you can further delineate the space using room separation lines, which will allow you to delimit areas without a physical element. For example, you can use a room separation line to create a divider between the living and dining areas in an open-concept space.
Room separation lines allow you to create different color schemes for each room or section within a larger space, making it easier to distinguish between different areas visually.
Once you have your rooms and room separation lines in place, you can start setting up the color scheme. In the Categories tree, under the Visibility tab, make sure the Color Fill option is selected. This will allow you to see the Revit color scheme applied to your model.
Now that you’ve set up the basic elements, you can follow these steps to create your custom color scheme:
The first step in creating a color scheme is to select a color-fill legend. This will act as the base for your color scheme and determine the overall color palette for your model.
Click on the Architecture tab> Room & Area panel drop-down> (Color Schemes) and then click on the Edit Scheme option to create a new scheme or modify an existing one.
In the Edit Color Scheme dialog, you’ll be asked to select a color scheme category. This will determine which categories of building components you want to apply the color scheme to.
You’ll need to pick from the following options:
If you already have an existing color scheme, you can select it from the list and modify it according to your needs. This is useful if you want to make small changes or add new colors without starting from scratch.
You can also right-click and click Duplicate to create a copy of the existing scheme and make changes to it without affecting the original. Or you can create a new scheme by clicking on the New option and naming your scheme.
Under the Scheme Definition field, you can add a title for your color-fill legend. This will help identify the scheme and its purpose. You’ll see this title above the legend when you apply the color scheme to your model.
Under the Color list, you can choose a parameter to base your color scheme on. You can add to or change these parameters later via the Properties Palette.
If you want to color by a specific parameter value or by a range of values, you can select the By Value or By Range options.
There are nine values that define how a color appears in the scheme, including:
Modifying these values will allow you to customize the color and appearance of each value in your color scheme.
With all your color scheme values set, click OK to save your changes and create your custom color scheme.
Once you’ve created a color fill legend, you can apply it to your model by following these steps:
Your model should now be visually enhanced with your custom Revit color scheme, making differentiating between different areas and sections easier.
Features the latest informative and technical content provided by our industry experts for designers, engineers, and construction firms and facility owners.
LEARN MORESTAY IN TOUCH